Water Reuse - Taking the 'Waste' out of Wastewater
The negative connotations of “waste” in the term “wastewater” deter many from thinking about it as a reusable resource.
Wastewater or “used water” is not just re-usable, it is a valuable resource that can contribute to poverty reduction efforts, food security and sustainable energy use. There is huge unrealised potential for economic gains, particularly in fast developing economies where water and resource scarcity is a major issue.

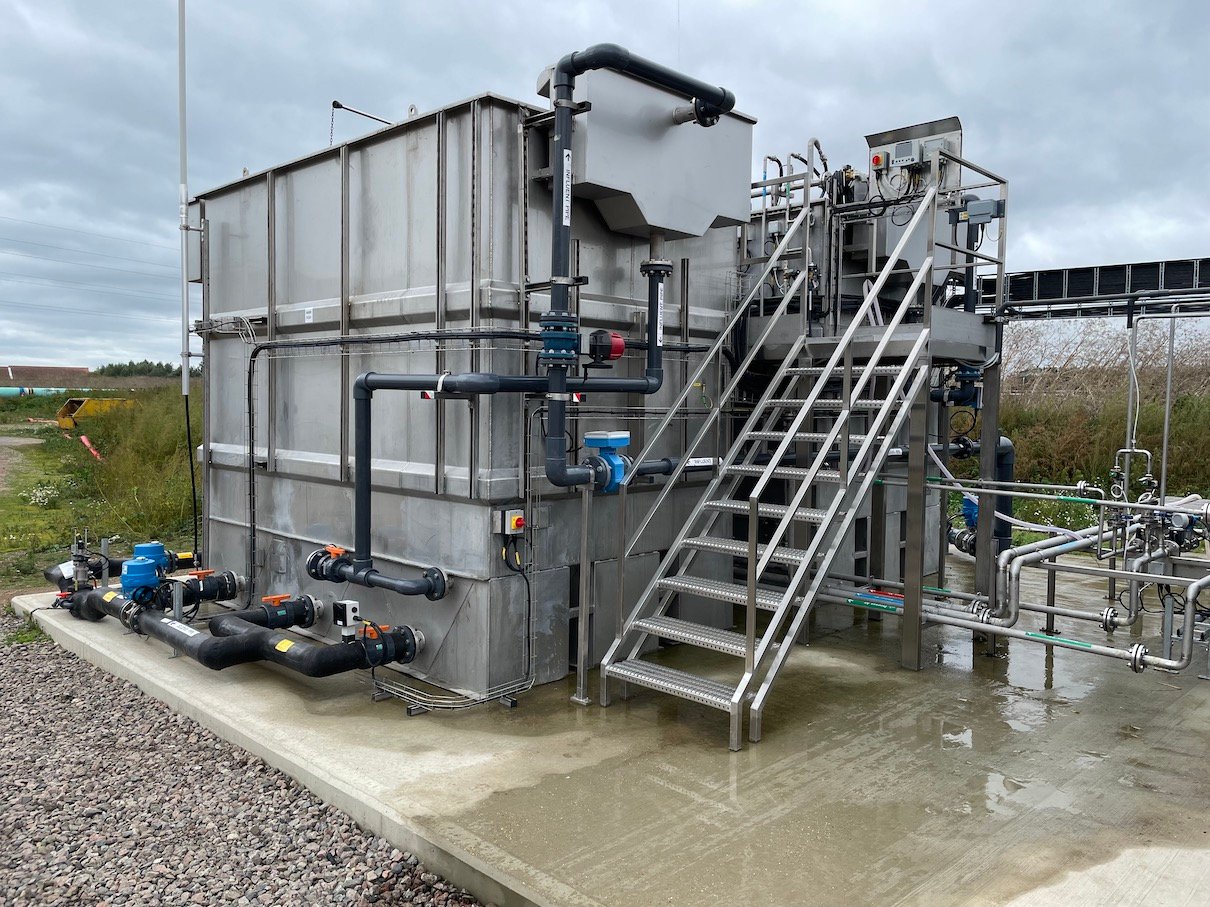
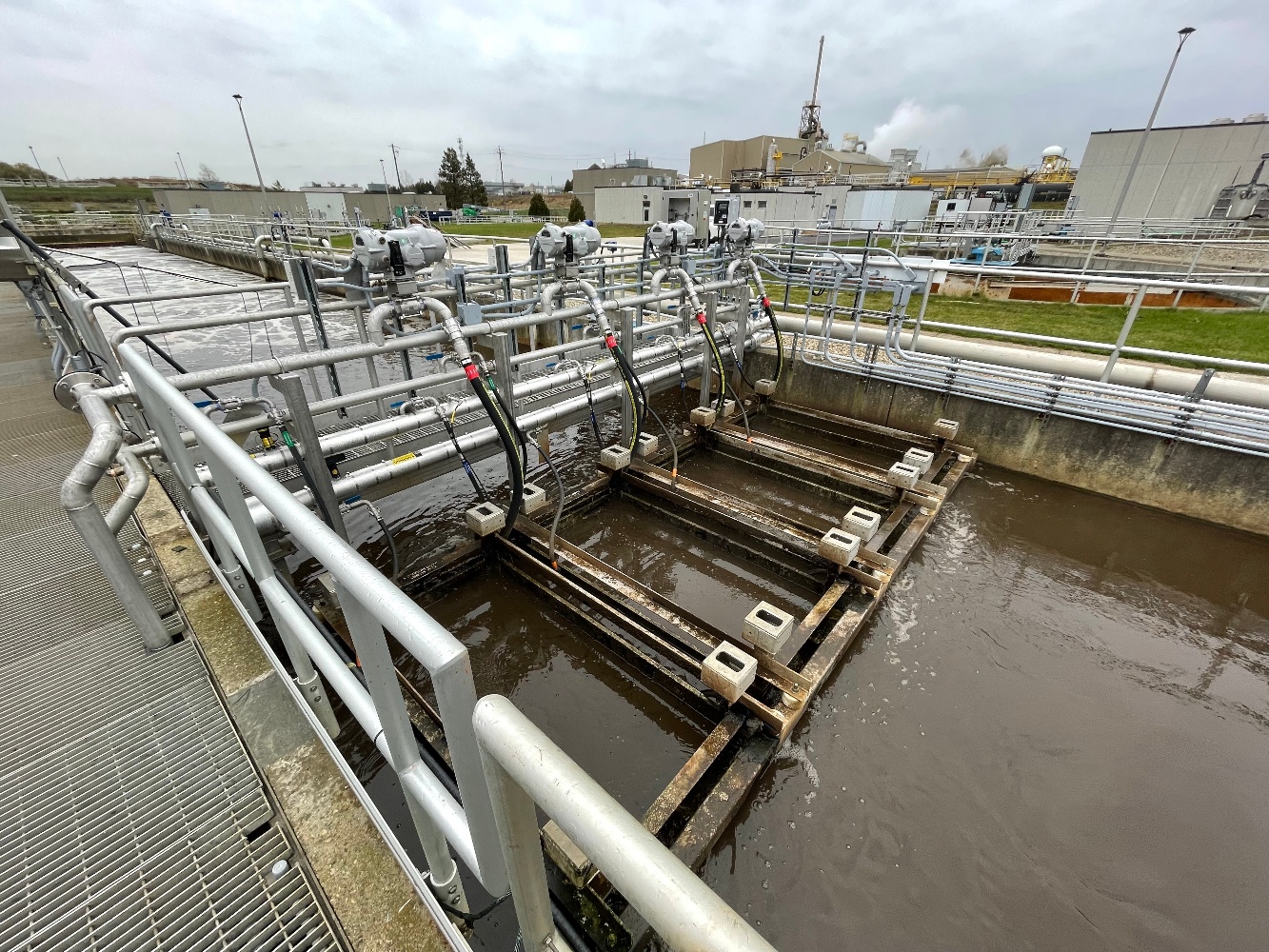
Wastewater treatment is a process which all governments are tackling. Untreated wastewater is an environmental and public health hazard, requiring appropriate intervention. However, treating wastewater is expensive and governments in developing countries have difficulty securing the required capital investment and covering long term operation and maintenance costs of treating this Wastewater.
But perhaps treatment of this used water isn’t as expensive as it seems especially when useable products can be produced. There are a number of innovative treatment technologies which are paving the way to reduce the operational expenditure of wastewater treatment for reusable water production. When reuse is considered, the products from wastewater (energy, biosolids and reusable water) have market value and address cost recovery.
Some wastewater treatment plants can produce 100 percent or more of their energy requirement on-site. Wastewater treatment plants collectively could potentially contribute to national electricity demand. This represents a tremendous opportunity for the wastewater industry.
Biosolids and/or biogases can be recovered and sold as fuel. New separation technologies are capable of extracting phosphates, alginates, and biopolymers from the waste stream, which can be sold to manufacturers.
Treated water from wastewater treatment plants has been successfully reused as water for irrigation, for washing of streets, flushing toilets and as cooling water for large refinery and petrochemical plants. Providing a sufficient cooling water supply from wastewater effluent has the potential to save millions of cubic meters of fresh potable water.
We have only skimmed the top of the many potential reuses in this post. It does beg the question, maybe there is no wastewater, just wasted water?