Wastewater Treatment Odours – Causes, Effects & Solutions
Wastewater Treatment Plant Odours Are Common.
Causes
Rising Temperatures
Temperatures are rising as we come into the summer months and with this, the temperature of the wastewater also increases. As a result, aerobic bacteria become more active and begin digesting BOD and other nutrients at a faster rate. The warmer the water becomes, the more active they are and the more oxygen they consume. This results in low dissolved oxygen.
Anoxic Zones
Low dissolved oxygen coupled with rising temperatures can lead to an increase in anoxic zones at the bottom of wastewater aeration basins. Anaerobic digestion releases sulphur dioxide, along with a variety of other noxious gases that are the causes of wastewater odour.
Effects
Treatment Deficiencies
Odour is often a sign that more anaerobic digestion is occurring than there should be. Given that aerobic digestion is a much faster process than anaerobic digestion, it is likely that the wastewater is being under-treated.
Unhappy staff and locals
When gases are released from wastewater treatment plants they result in a very pungent odour which will directly affect WWTP operators and, when carried by winds, to people who live or work nearby.
Solutions
Increase Oxygen Supply
Increasing oxygen supply ensures that the aerobic bacteria have the oxygen they need to aerobically digest BOD. This will help to control odours as anaerobic digestion will slow down.
Wastewater Circulation
Ensuring dissolved oxygen is reaching the very bottom of an aeration basin is key to avoiding odour as this is where the odour-causing anaerobic digestion occurs. By circulating the wastewater effectively, you can create nearly equal dissolved oxygen throughout. This in turn will promote odour-free aerobic digestion.
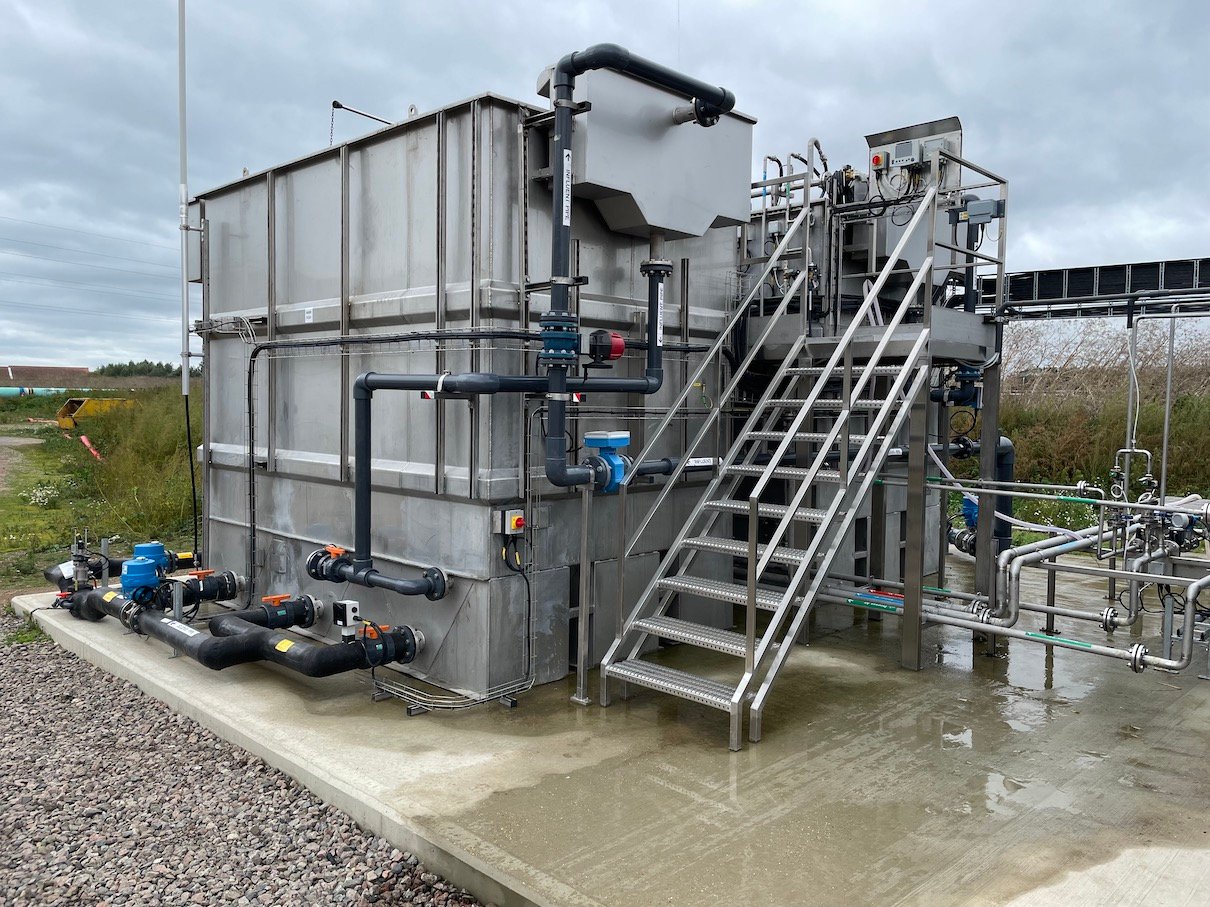
Aeration technologies currently in use are not always effective at increasing oxygen supply and ensuring circulation throughout. Surface aerators only circulate to a shallow depth of the water column and do not increase dissolved oxygen in deeper water bodies. Coarse and fine bubble diffusers do a better job of increasing dissolved oxygen but struggle in combating anoxic zones. The OxyMem MABR can achieve up to 99% oxygen transfer efficiency, produces up to 50% less sludge than current technologies and in turn, reduces odour significantly.
In summary, treatment plants collects effluent flow from municipal and industrial sources for treatment. The level of treatment from each plant varies, but the one thing they all have in common is that they cause a smell!