OxyMem modules provide wastewater treatment plants with the simplest installation and easiest maintenance of any solution, enabling them to increase their capacity and effluent quality.
Each OxyMem module comes with essential features as standard, to ensure ease of use, effortless maintenance and a consistently high performance.
The Airlift is part of every module produced and provides effective mixing using the off-gas from the membranes.
It is important to know what is happening inside the module at any stage, without the hassle of removing modules. Our easy to use biofilm measurement tool lets you know when to take action and how it is performing.
Connections are made for a blower to be attached that reduces the amount of biofilm in the module system.
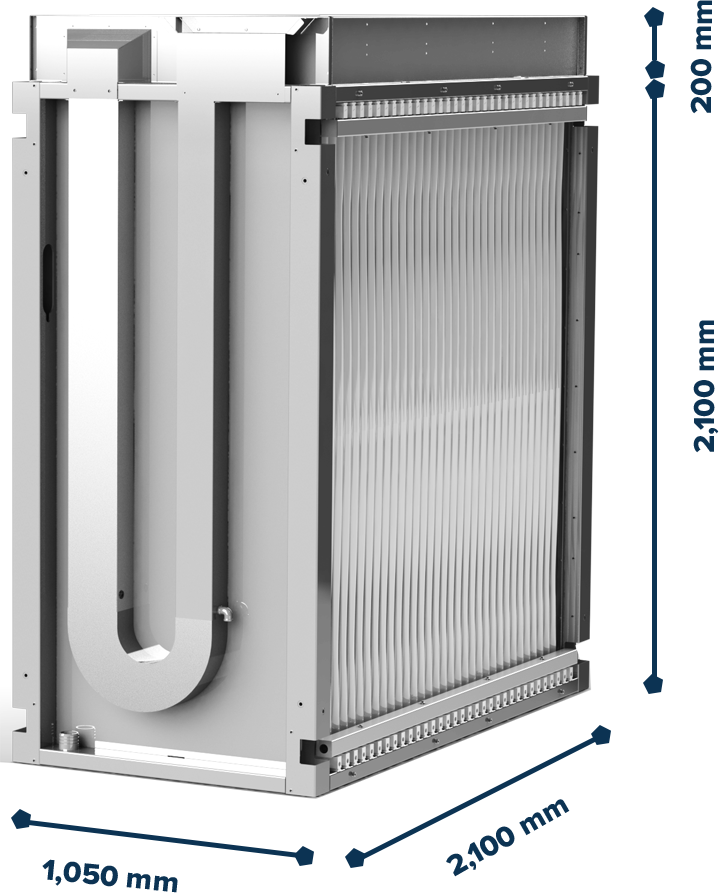
Each module comes with a module to module / blower connection meaning that one blower can power many different modules.
On all sides of the module we ensure that once wastewater reaches the inside of the module we gain maximum contact with biofilm and pollutants whilst maintaining flexibility of access to inside.
In the unlikelihood that wastewater does get into the membrane system through a tear on a membrane the purge tool will remove any unwanted content and biofilm will cover leakage.
The OxyMem MABR modules can be easily dropped into existing aeration basins without draining the tank or interfering with the current processes.
When fitting the module in an existing tank a single stack a wall mounted system can be used which does not require the tank to be drained as the work can be carried out outside the tank using additional bracketry.
The installation process can be completed in a matter of days all that is required is the MABR module is connected to the scour and the process blower- no additional land or infrastructure is required.
There are several ways in which the modules may be deployed i.e. they can be attached to the side of the tank, raised from the bottom or hang from the centre. The modules can also be stacked horizontally or vertically giving you added performance with each unit.
Example installation

Short circuiting in wastewater plants occurs when some wastewater enters the tank and exists via the effluent outlet without being treated. The prevention of short circuiting is key to the prevention of eutrophication in rivers, lakes and streams.
Our experienced team combined with the powerful airlift mixing tool on all our MABR modules avoid short circuiting with our added ability to control the flow direction of wastewater in the tank. The airlift mixer allows us to draw water from the bottom of the tank and create a serpentine or unidirectional flow. This control ensures that all wastewater in the tank receives the optimal contact with the biofilm that removes the pollutants before it reaches the effluent outlet.
OxyMem uses a patented biofilm measurement technique, which determines an effective biofilm thickness on the membrane. When the control system determines that the biofilm has grown too thick for the treatment process required, the system takes steps to automatically remove the excess biofilm.
As biofilm grows from the membranes the older biofilm exists on the outer layer of the membranes as this is reaching the end of its life span and it does not consume pollutants as well as it did at earlier stages. The closest biofilm area to the membrane is in a development stage and does not consume a lot at the beginning. The middles layer of biofilm is at peak performance and removes pollutants more effectively. OxyMem provides a measurement tool to know when to remove the under-performing biofilm. Excess biofilm on the membranes is removed by using intensive short duration scour. This prevents clogging and maximises performance.
The frequency of cleaning is dependent on the growth rate of the biofilm and the nature of the treatment process but can vary from once a day to once every two weeks. Self-cleaning will typically last 1-2 mins in duration so the energy burden is negligible.
Maintaining a consistently high level of COD Removal, Ammonia Removal, Nitrite Removal and Nitrate Removal makes OxyMem the clear winner when it comes to keeping with effluent compliance standards in different climates and with seasonal changes in load.
Where suspended biomass wastewater treatment plants may find it difficult to nitrify during the winter months, the OxyMem MABR continues to treat with optimum performance. The biofilm required to treat the wastewater is maintained within the biological treatment zone, securely attached to the extensive membrane surface area. With this arrangement, important nitrifiers are maintained within the system and are not washed out during peak wet weather flows.
OxyMem have continued to nitrify and denitrify with relative ease during winter conditions in Canada, Spain and Denmark.
The MABR modules tackle seasonal changes by stabilising the amount of COD in the effluent. In some cases we have decreased the average COD/d by 75% and kept it consistently at this rate. This consistency provides wastewater plants with a buffer, providing room for more capacity and peace of mind knowing that they will avoid any breaches in regulation.
The MABR modules also have a huge effect on activated sludge properties allowing plants to maintain a consistently low effluent TSS kg/d concentration.
Performance measurement is key for measuring return on investment and understanding how well your plant meets regulatory standards.
The OxyMem MABR Modules come with an abundance of testing options to add on however the clearest indicator that the Module is performing is by testing the oxygen levels of the air entering the membranes vs the oxygen level of air exiting. This gives a clear indication of the Oxygen Transfer Rates that is quick and easy.
It is critical that wastewater treatment plants reduce the amount of organic matter in the wastewater before it is discharged back into the rivers and lakes. If there is excess biological matter in the wastewater it can have damaging effect on the receiving waters as it will consume the oxygen in the water and harm the fish and ecosystem.
Wastewater treatment plants need to test the wastewater before it is released back into the environment to ensure that it is sufficiently treated. There are several different metrics which can be used; Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a measure the total organic matter in the wastewater. It includes both the biodegradable and non-biodegradable matter. It is expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre (mg/L).
COD = MG O²/L
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) measures only the biodegradable matter in the wastewater. Chemical Oxygen demand is always a higher result.
Due to the constraints testing Biochemical Oxygen Demand, Chemical Oxygen Demand is a more commonly used for testing the effectiveness of the wastewater treatment. The test is used by the industry as it can be carried out in a couple of hours whereas the BOD test which can take 5 days.
If the COD result is high it can indicate that there are issues with the wastewater treatment that need to be addressed. As the test is done quickly it allows for issues to be addressed as they occur. The higher the level of COD the more polluted the water is.
© Copyright 2017-19, OxyMem Limited | Company Registration No. 530400 | VAT Registration No. IE3192612NH | INBS