OxyMem MABR – The Fixed Film Revolution
Wastewater treatment is OPEX intensive
A century has passed since the introduction of the Activated Sludge process – but how far have we come in terms of improving, innovation, developing and innovating for the challenges of today? Nowadays the activated sludge process is one of the most widely used wastewater treatment processes worldwide. It successfully treats municipal and industrial wastewaters and has returned water and river quality to a high standard on a global scale. However, the water-energy nexus discussion has begun in earnest and we are faced with a wastewater infrastructure crisis to serve growing pressure to answer the arising issues. How do we combat the amounts of energy and other operational expenditure it takes to collect, move, treat and discharge water? How do we move the dial to energy neutral wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is OPEX intensive
Close to a quarter of operational expenditure for wastewater treatment is attributable to electricity demand. Sludge transport & disposal and staff costs make up a further quarter each with maintenance, chemicals and discharge fees making up the rest of the contributing operational costs. When it comes to energy use, an incredible 57% of electricity is needed for the aeration of wastewater.
Since 1913, bubbles have been the preferred delivery system of oxygen to organic degrading bacteria in wastewater. Although there have been many improvements in the diffusers used since its introduction, from coarse bubbles to fine bubble diffusion in the 1970s to ultrafine and nano bubble delivery in the late 90s, there is still a 60 – 70% energy waste as the bubble has a limited life span in an aeration tank.
Fixed Film Evolution
Since the late 1800’s fixed film systems have been in use and are still depolyed extensively around the world today leading to over 120 years of fixed film technology. They have been successful due to their robust and reliable nature as well as their ease to install and operate. However, the market has in the last 30-40 years found the energy costs a challenge when using these systems at any scale. The main technologies today that use this include MBBR, IFAS, RBC. To improve reaction rates they combine mechanical and bubble aeration. OxyMem MABR is a fixed film technology that doesn’t use conventional aeration.
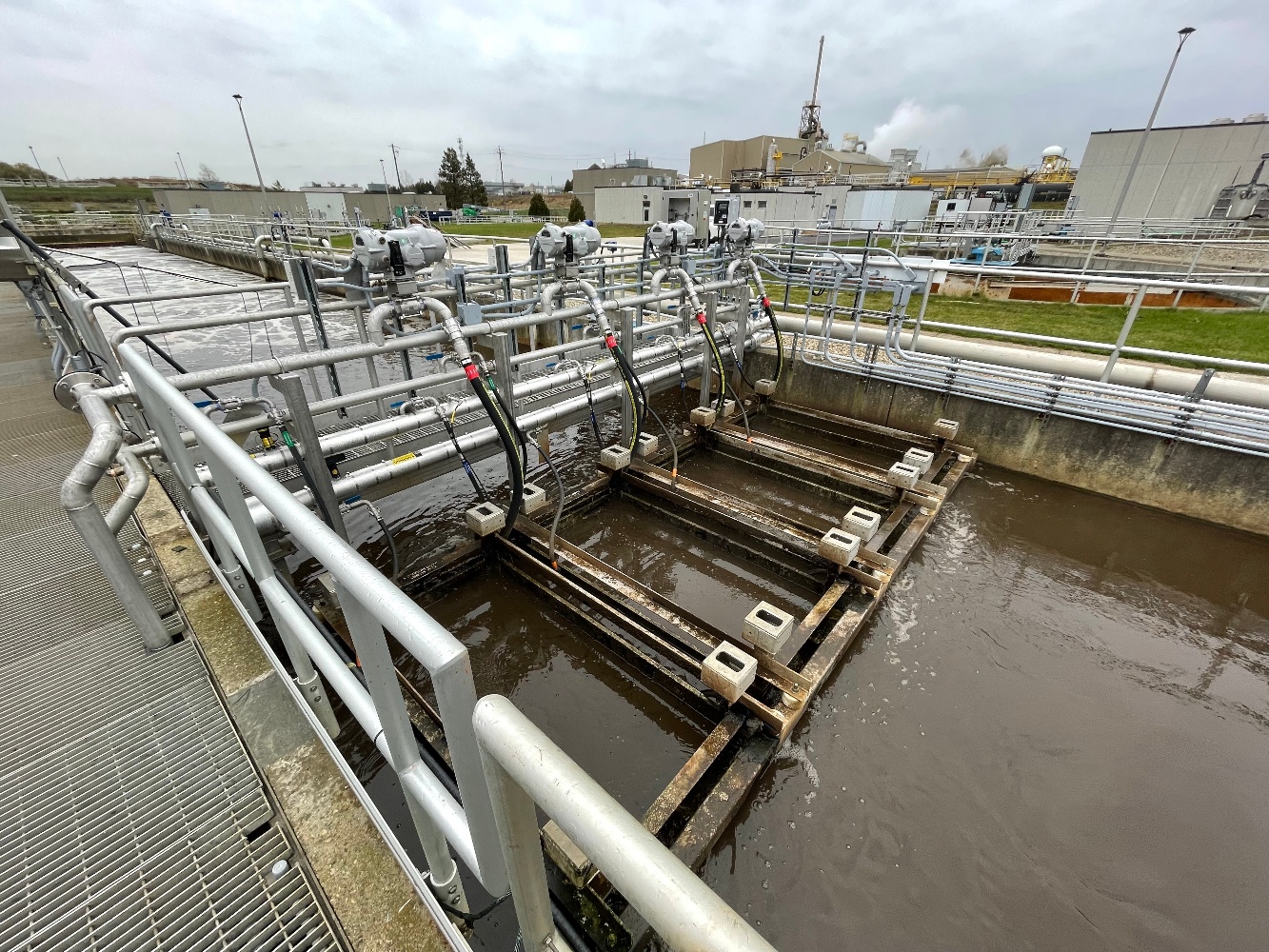
Smarter Media, The Fixed Film Revolution....
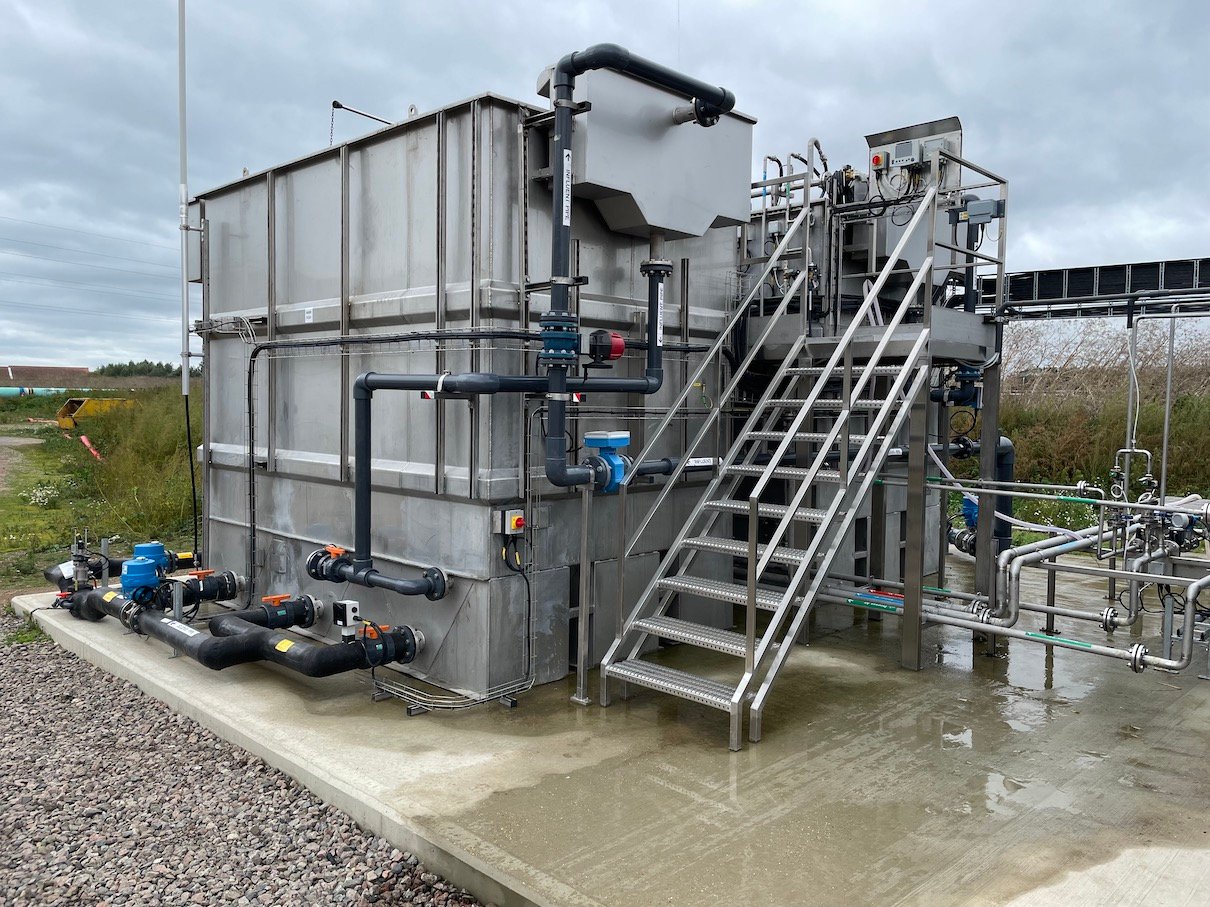
Manufactured in house at the OxyMem headquarters in the Irish midlands, the smart fixed film media is made from PDMS (silicone), a dense membrane with a life span of up to 20 years. The technology needs no chemical dosing, is low cost and gives significant scope for performance improvement.
In comparison to conventional systems, OxyMem unlocks the potential of fixed film technology. Biofilm activity is not limited to the biofilm surface with the OxyMem media able to achieve 100% aerobic activity. This high reaction rate results in a very low energy intensity and gives the ability to affect different treatment outcomes. For the first time – a pathway for energy neutrality in wastewater treatment is now possible.