OxyMem, Boldly Going Where No Sewage Treatment Has Gone Before!
NASA is hard at work tackling the challenges of space travel and dreaming up technologies to meet those challenges.
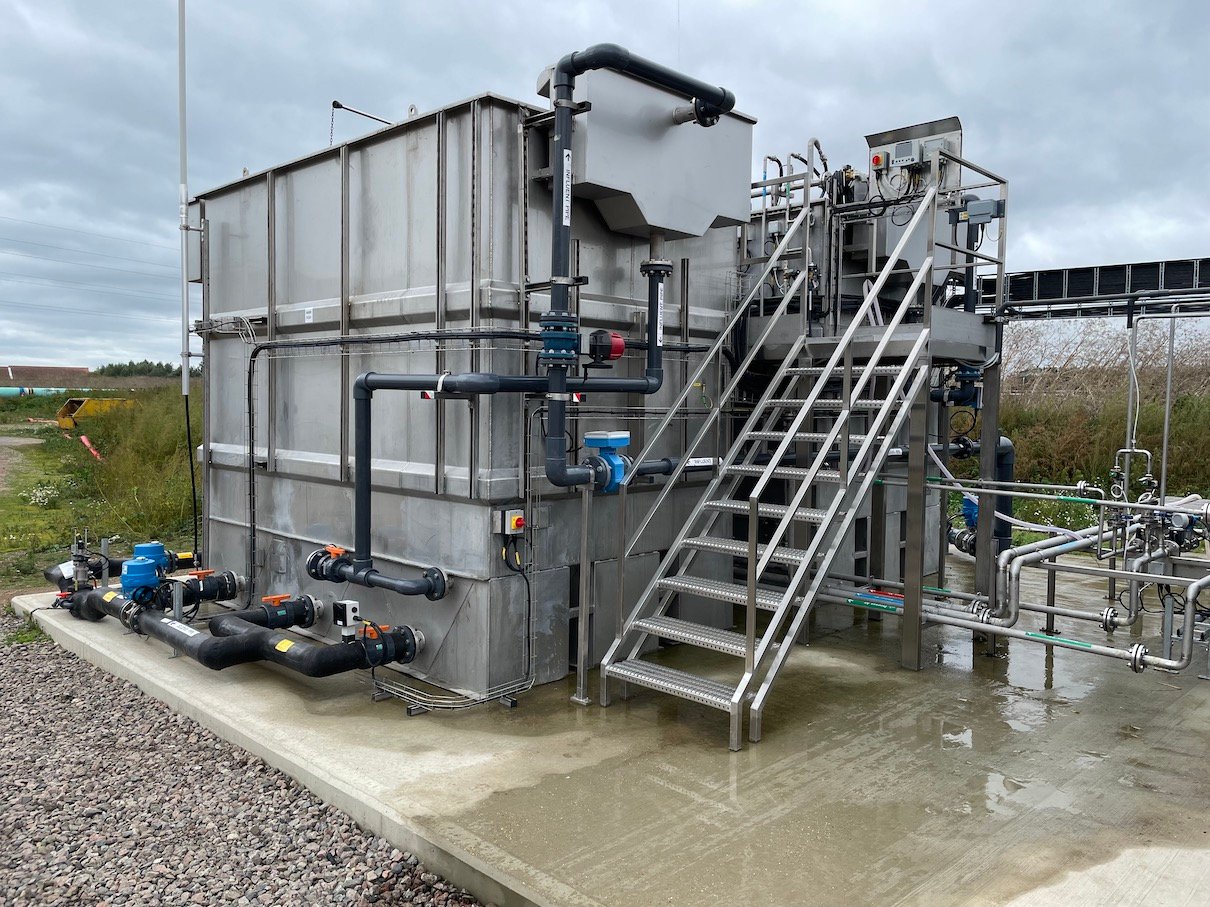
Researchers are examining wastewater recovery systems robust enough for use on long term space missions. Biological treatment has been the primary focus, with specific thrusts in developing a biological treatment system that may be operated with minimal crew maintenance and low energy and mass requirements.
In space travel, water is crucial. As space agencies around the world are contemplating human missions to Mars and even further afield, water must be recovered aboard the spaceship.

Currently, water in space-stations is produced by the condensation of humidity and by the treatment of urine excreted by astronauts. This waste is recycled using a combination of membrane filtration and distillation processes however on long voyages, such as those to Mars, there will be no ability to supply replacement filters from earth or to dispose of concentrated waste streams.
Biological wastewater treatment degrades pollutants, produces less waste and at the same time uses less energy and no chemicals. This makes it a serious contender for a role in the recovery of water aboard long duration space missions.
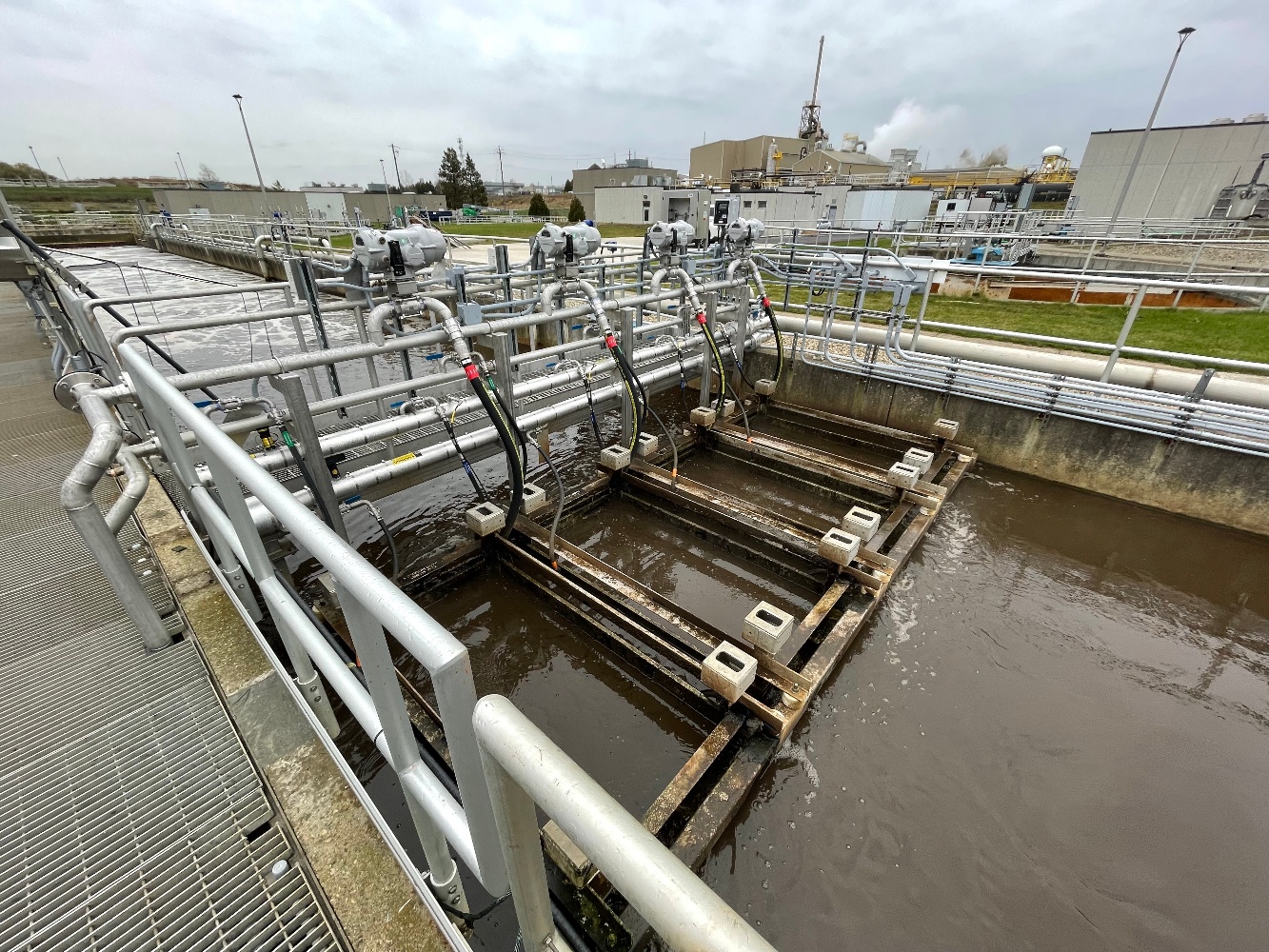
Microgravity conditions in space mean that bubbles don’t work, so an alternative method of supplying oxygen for the biological treatment is required. The Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor supplies Oxygen through concentration gradient across the gas permeable membrane without the requirement for gravity, therefore allowing for the aerobic biological degradation of the waste.
Additionally because the process is biofilm based it is more stable and resilient than suspended biological treatment processes, which is crucial when the nearest help is 200,000,000 km away.
In a recent study by researchers at Texas Tech University it was concluded that the ability of an MABR using microporous membranes to perform as a treatment system was a “promising technology for use in space applications”.
With that in mind, could OxyMem - the first commercially available MABR on earth, one day make it into space? Only time will tell.